|
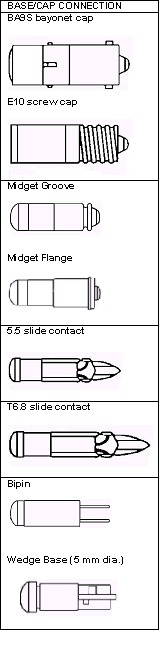
Base/Cap
Connection |
BINAY Multichip LED lamps are constructed
to the same physical dimensions as the existing filament bulbs, and
can be used to make direct replacements in the existing holders.
They provide an average life of more than 50,000 hours under normal
use, thus requiring no further replacement once fitted (as such,
they are a ONE-TIME EXPENSE). They have very low current
consumption, a vibration-resistant construction, and can withstand a
wide range of fluctuations in input voltage.
These bulbs incorporate
multiple P-N junction LED chips mounted on a ceramic or DMC header,
along with appropriate voltage and current controlling circuitry.
These chips are attached to a special substrate by a die-attaching
solution, after which they are thermosonically bonded to a fine wire
by means of a special bonder; the other end of the wire is then
bonded on to the substrate. The assembly is then encapsulated in
clear optical grade epoxy. The chips are connected in series (or
series-parallel combinations), and an appropriate impedance is used
to drop the balance of the applied voltage. The entire assembly is
mounted in a base (cap) similar to the existing filament
bulb.
The use of very high
intensity chips enables the manufacture of multichip LED lamps in
low current versions in 6V, 12V, 24V, 48V, 60V, and even in 110V and
230V ratings. A significant advantage of the use of these high
diffusion chips is the improved light dispersion possible. Multichip
construction provides extremely wide-angle and dispersed light
emission (as compared to discrete 3mm or 5mm LEDs). As such, these
multichip LED lamps are ideal for use in applications such as
annunciator window fascias and illuminated pushbutton switches
(which require effective wide-angle backlighting of inscribed
legends).
The use of ceramic or
DMC substrates in the construction is of particular importance, as
this allows rapid heat dissipation of the heat generated in the
chip. BINAY Multichip LED lamps are NOT constructed with plastic
substrates (as plastic will trap the heat inside the chip, resulting
in heat build-up and subsequent premature chip failure).
BINAY Multichip LED
bulbs are available in a variety of different dimensions and bases
(caps), such as BA7S, BA9S, B15 (bayonet); midget groove, midget
flange; 5530 and 6844 telephone (slide contact) type; bipin; wedge
base; E10, E12, E!4 (screw cap base).
The following data is
required to correctly specify a proper multichip lamp
replacement:
| Cap/base type |
Polarity of contact – i.e., centre point positive/body
negative, OR centre point negative/body positive (for BA9S,
E10, Midget Groove and Midget Flange caps) |
| Exact
voltage rating |
| Colour |
| AC or
DC |
NOTE ON UTILISATION :
These multichip LED lamps will generally have lower current ratings
than the existing filament bulb they are replacing. Occasionally, in
some situations, the existing filament bulb is operated at a lower
voltage which is derived from a higher voltage by dropping through
an external series resistor. In such cases, the current rating of
the existing bulb circuit becomes important, since the voltage
dropped in the external series resistor will be dependent on the
current passed through the resistor (V across the resistor = I x R).
If a multichip LED lamp of lower current is installed in such a
position, the voltage drop across the external series resistor will
be very much lower due to the lower current rating of the LED
multichip lamp, leaving a high remainder voltage to be applied to
the multichip LED lamp. This will cause the multichip lamp to be
overloaded, affecting its performance. For such positions, we can
design a suitable multichip LED lamp replacement if the following
data is provided to us.
- The initial higher voltage (which
is dropped through external series resistor to provide the lower
voltage for the lamp)
- The value of the external series
resistor in ohms
|